Irregular Mare Patches (IMPs) are a group of small depressions distributed in the nearside of lunar maria. Accurate understanding of its geological features and origin will provide direct key constraints on the cessation time of lunar volcanism and strengthen our knowledge of lunar geologic and thermal evolution history. Due to the unusual and complex characteristics of IMPs, the study of their geological features is still very weak. There is a lack of research on the classification of IMPs, and its specific formation mechanism is debated.
Le Qiao et al., associate researcher of Shandong University, who firstly undertook an updated search and geological characterization of all IMPs and established an updated catalog of 91 IMPs. Then, a detailed survey of the geologic context and internal structure of each IMP was carried out based on high-resolution images and topographic data of the lunar surface. Two classification schemes were established: (1) geologic context: IMPs are categorized into (a) small shield volcano summit pit floor and flank, (b) linear/sinuous rille interior and adjacent exterior, and (c) typical maria; (2) characteristics: IMPs are classified into (a) “mound + floor” and (b) “pit only” types. We believe that the series of very complex geological features of IMPs can basically be explained by the "late magma foam eruption" model, but there are still a series of outstanding problems that have not been resolved, which need to be explored by future lunar exploration and research.
The research results were published in Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
Qiao, L., Head, JW, Ling, Z., Wilson, L., 2020. Lunar irregular mare patches (IMPs): Classification, characteristics, geologic settings, updated catalog, origin and outstanding questions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets , in press, doi: 10.1029/2019JE006362.
Link: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2019JE006362
This study is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 41703063, 11941001, and 41972322), a Pre‐research Project on Civil Aerospace Technologies no. D020205 funded by CNSA, the grant from Key Laboratory of Lunar and Deep Space Exploration, CAS (no. LDSE201902), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (nos. 2017M610421 and 2018T110682), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019MD008).
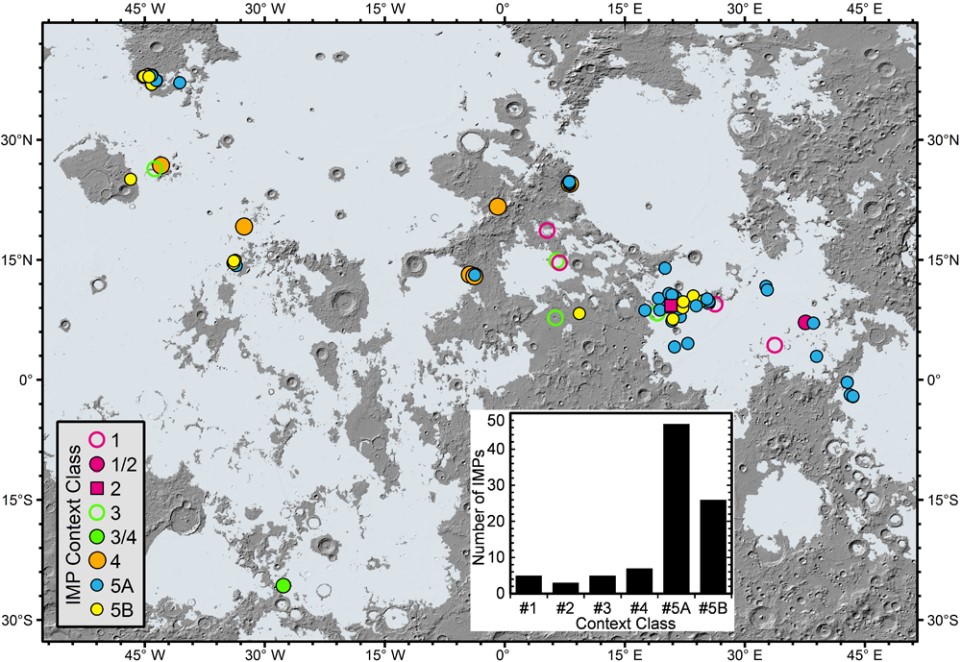
Figure 1. Spatial distribution of all identified IMPs in terms of the classification of their geologic context.
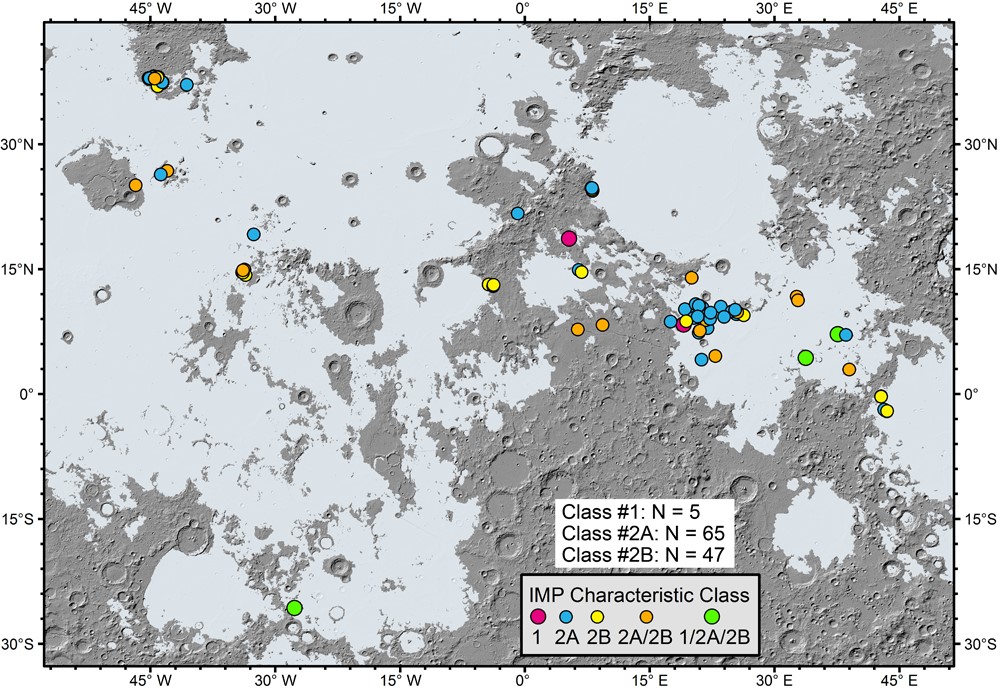
Figure 2. Spatial distribution of all identified IMPs in terms of the classification of their characteristics and structure.