As the largest confirmed impact basin on the Moon, SPA basin is thought to have penetrated into lunar interior and excavated deep materials from lower crust and upper mantle during its formation. Since global remote sensing enabled observations of the lunar farside, observations of the SPA basin floor indicate that it is characterized by mafic anomaly, which is mainly composed of norite enriched with low-Ca pyroxene (LCP, orthopyroxene (OPX) or pigeonite)-rich. The nature of mafic anomaly in the floor of SPA basin, which exhibits distinct geochemical and spectral characteristics from returned lunar samples and currently known lunar meteorites, is regarded as an ideal indicator of the composition and mineralogy of lunar interior.
The CE-4 landing site is located on the floor of ancient Pre-Nectarian Von Kármán crater and mostly overprinted by discontinuous ejecta from the nearby Finsen crater in the northeast. The ejecta, characterized by non-mare mafic components in orbital remote sensing datasets, exhibits pervasive mineralogical similarities to the mafic anomaly observed in the central portion of SPA basin. Yutu-2 rover provide a valuable opportunity to improve our understanding of the unusual mineralogy in the floor of SPA basin.
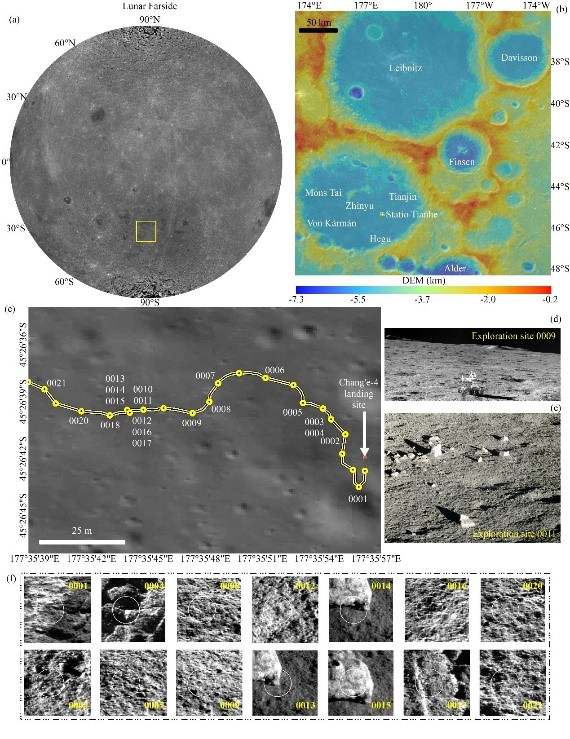
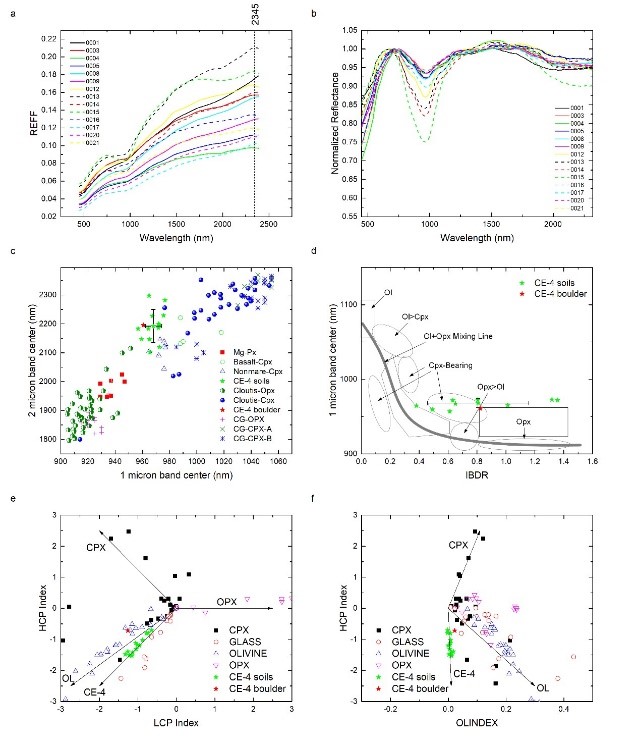
This study aims to develop a systematic VNIS data processing strategy and report preliminary analysis results in terms of mineralogical information of the exploration region of Yutu-2 rover in the first three lunar days. The mafic components in the soils and boulder around CE-4 landing site are concluded as clinopyroxene-bearing with intermediate composition and probably dominated by pigeonite, although mixing effect of OPX and calcic CPX cannot be excluded. The CE-4 regolith and rock fragment are believed to derive from rapid-cooling magmatic systems (basaltic lava flow or impact melt) and we interpret that that the materials at the CE-4 landing site ejected from Finsen crater are probably recrystallized from impact melt settings.
Paper published in "Science China Information Sciences"
Link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-019-2768-1
Chen, J., Ling, Z., Qiao, L. et al. Mineralogy of Chang’e-4 landing site: preliminary results of visible and near-infrared imaging spectrometer. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 63, 140903 (2020).
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11941001, 41972322, U1931211), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR2019MD008), Qilu Young Scholar (TANG SCHOLAR) Program of Shandong University, Weihai (Grant No. 2015WHWLJH14), Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. QYZDY-SSW-DQC028), and Pre-research Project on Civil Aerospace Technologies Funded by China National Space Administration (CNSA) (Grant No. D020102).